Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Great Website Speed Disconnect
- Why Are So Many WordPress Websites Slow?
- Common Reasons Behind Slow Load Times Of WordPress Websites
- Checking WordPress Website Speed
- WordPress Website Best Practices To Ensure Optimum Performance
- Be Careful While Choosing Hosting Plan And Provider
- Choose A Theme Optimized For Speed
- Maintain A Clean Database
- Maintain A Clean Media Library
- Make Sure Everything Is Updated
- Get Rid Of Bad Plugins
- Use A Content Delivery Network (CDN)
- Use Hosting Platforms For Videos
- Use Excerpts
- Split Comments Into Different Pages
- Limit Post Revisions
- WordPress Website Speed Optimization Tips
- Optimize Images For Speed
- Minify JavaScript, HTML, and CSS Files
- Remove Render-Blocking For JavaScript and CSS
- Move Database Tables To InnoDB
- Install A Caching Plugin
- Reduce The Number Of External Scripts
- GZIP Compression
- Disable Pingbacks and Trackbacks
- Lazy-Load Long Pages
- Split Long Posts Into Different Pages
- Use The Latest Version Of PHP
- Conclusion
Introduction
The web has invaded almost every aspect of our lives. In some cases, the invasion is a welcome one, as it has made our lives easier. Delivery services, streaming websites, search engines, and many other types of websites fall into this category.
However, we have become so dependent on the web that our usage patterns have started altering the way we react to things. One instance of the same is that the web has made us impatient.
Remember the days of dial-up internet? We would sometimes have to wait several minutes for an image to load on a website, and we were simply so intrigued by what the web can do, that we did not mind waiting. Today, that has changed, dramatically.
Today, the users on the web are a lot more impatient. A 2017 Google study revealed that when a website page load time increases from 1 second to 3 seconds, the probability of a bounce (user leaving immediately) increases by 32%. The same study revealed that most users expect all sites to load within 3 seconds.
This trend has made the load speed of their website a big concern for many website owners, especially those whose website is their primary source of revenue.
Yet, there is a serious disconnect between the users’ expectations of how quickly a website should load and the real-world website load times.
The Great Website Speed Disconnect
Despite the well-known diminishing patience of users, websites with most industries have failed to keep up with user expectations. A 2019 analysis of 5 million web pages by Backlinko revealed that the average load time for web pages (across industries) on desktops was 10.3 seconds. If you think that’s bad, the average load time for the same websites on mobile devices is a staggering 27.3 seconds.
User expectations is not the only reason website speed should be a concern for you. Even Google has made it known that they consider website speed as a ranking factor, placing faster websites higher than their slower competition.
For visionary entrepreneurs, there lies an opportunity in these stats. An opportunity to stand out from the noise of competition with a delightful and lightning fast website experience. However, delivering that with WordPress, as awesome as the platform is, is not always easy. Let’s look at why:
Why Are So Many WordPress Websites Slow?
WordPress is an amazing platform that has enabled beginners with no experience to build amazing websites. The platform is intuitive and user-friendly. These features, combined with the dependability it offers, have made WordPress the most popular content management system on the web.
As of 2021, WordPress powers 75 million websites. That enormous number accounts for more than 30% of all websites that are live on the web. Not surprisingly, this number is expected to jump the 100 million mark in the coming years.
With so many people using WordPress, the platform has created its own mini-economy that thrives on the sale of plugins, tools, and themes that are all designed to further boost the potential of WordPress websites.
Yet, many WordPress users find themselves struggling with the question “Why is my wordpress site so slow?”
While a lot of these plugins, themes, and tools are incredibly useful, there are also several that will hurt the load speed of your WordPress website. Every time a user loads a page of your website, they are just loading a page. However, in order to display the page to the user, the browser must first load all the elements (including plugins) operating on that web page.
With that said, while the number and quality of the plugins and themes used with various websites have the potential to slow them down, there are other reasons that can slow down a website.
Common Reasons Behind Slow Load Times Of WordPress Websites
Having worked with a variety of clients from different industries, we’ve discovered some pretty unique reasons behind slow load speeds of WordPress websites. However, more often than not, one or a combination of the following reasons is behind the slow page load speed of a WordPress website:
- Poor WordPress Configuration: One of the best ways to serve content faster and reduce load on your server is to serve cached content. However, if your website is not optimized for the same, not only would the load times be slower, there is also a chance that your website might crash altogether.
- Web Hosting: If your web hosting is not configured properly, or if you don’t have the right kind of hosting plan to support your website, it can seriously hurt your website’s load speed.
- Images Not Optimized: If your website images are not optimized for speed, they are likely to negatively affect the load times.
- Bad Plugins/Bad Theme: As mentioned earlier, badly coded plugins and themes that aren’t optimized for speed are one of the most common reasons behind poor load times for WordPress websites.
- External Scripts: One of the most commonly operating external scripts on WordPress websites are ad scripts and the wrong ones can have a negative influence on your website page speed.
So how can you figure out what is slowing down your website?
Checking WordPress Website Speed
A lot of beginner WordPress website owners tend to think that since their website loads quickly on their devices, it does not have a speed related issue. However, that is usually a misconception. When you frequently visit a website, your browser presents you with a cache of your website that it starts preloading as soon as you start typing the name of the website. This does not happen when a new user is visiting your website for the first time and for them, the website may take a lot longer to load.
Figuring out how your website is truly performing is the first step to speed up WordPress websites enough to delight visitors. Thankfully, there are a number of online tools that will help you in this matter, for free.
One of the most popular tools to test website speed is developed by Google, known as Google PageSpeed Insights. The tool is free to use and offers actionable insight into making any website faster.
With that said, there are also a number of great page speed testing tools that are designed specifically for WordPress websites. My top three recommendations are the speed testing tools by WPengine, Isitwp, and GTMetrix.
The results on these platforms are usually accompanied with actionable advice about how you can improve the speed of your website. However, if you are a beginner, there might be a lot of terms and phrases that you may not understand. If that is the case, don’t worry. Everything that is commonly highlighted in these speed tests will be discussed in sections of the article that follow.
Now that we know how you can check the speed of your WordPress website, and the common reasons that may be slowing it down, let’s look at a few WordPress best practices that will help you ensure your website keeps delivering optimum performance.
WordPress Website Best Practices To Ensure Optimum Performance
The tips shared in this section are not meant for WordPress speed optimization.
Instead, this section is dedicated to ensuring your WordPress website is configured correctly so that the speed optimization strategies that will be shared in the sections that follow will work as they are intended.
Let’s jump right into it:
Be Careful While Choosing Hosting Plan And Provider
Hosting is a service that allows you to store your website’s data on someone else’s server. Your hosting provider owns one or multiple data centers that are home to a server that ultimately store all the files related to your website (content, images, videos). This way, you can access, manage, and update this data easily and it can be quickly served to your website visitors.
Keeping all that in mind, it is not difficult to imagine how your choice of hosting plan and provider can have a big influence on your website’s performance. There are three popular hosting types you can choose for your WordPress website:
Shared Hosting
This is the option that most beginners go for, mostly because it is the cheapest option. Shared hosting plans start at as little as $3 and are offered by well-known companies like HostGator, GoDaddy, BlueHost, and other similar brands. To boost sales, shared hosting plans are usually available at heavily discounted prices, especially for first-time customers.While all that may make them a lucrative option, take a minute to think how these companies are making profit off of your $3. In exchange for that money, you aren’t just getting space on a server, you are also getting customer support from real humans. $3 doesn’t even begin to cover those expenses. Yet, many companies offer ‘unlimited resources’ plans to their customers.So, to make up for this low cost of their service, and to maximise profit, these companies make several clients ‘share’ the same server. On an average, a shared hosting server is hosting around 200 different websites. Out of these 200 customers, whoever consumes the most resources starts hitting the limit of the server and starts facing problems that sometimes include site suspensions. When they leave as dissatisfied, they make space for more customers that will hopefully not demand as many resources.Bottom line, if you are making consistent efforts to bring more traffic to your website, shared hosting will fail you at some point.Another way that shared hosting providers make profits is with hidden charges for services that are necessary, like SSL certificates, migrations, and domain registration. In other words, if transparency and performance matters to you, shared hosting is probably not the right choice
DIY VPS Hosting
DIY VPS stands for Do It Yourself On A Virtual Server and the terms are pretty self-explanatory.With this kind of plan, your website gets to live on its own private virtual server, away from the problems of shared hosting. In exchange, you are expected to pay only a slightly more than what one would pay for shared hosting. Most DIY VPS plans cost between $5 and $15, depending on the requirements of your website.The only catch is, you are responsible for maintaining your server and keeping it secure. The DIY approach here is great for those who are looking to save money and have the technical knowledge required to manage a server and optimize its performance.If, however, you don’t have that kind of technical expertise on your team, choosing this plan is not advisable, not even if you are thinking of experimentation.
Managed WordPress Hosting
Managed WordPress hosting service combines the best aspects of DIY VPS and shared hosting services, while getting rid of their limitations as well.Like DIY VPS, you get private server space for your website but unlike DIY VPS, you don’t have to manage it yourself. Instead, you get complete and thorough server-related support and optimization handled for you, by a team of certified support professionals. Since most managed WordPress hosting providers exclusively work with WordPress websites, these support executives accumulate truly in-depth knowledge of servers and WordPress websites.These features make managed WordPress hosting more expensive than other types of hosting plans but the extra investment is definitely worth it. That’s why most big companies and websites that get a lot of traffic choose this type of hosting.Managed WordPress hosting services start at around $25 a month and may go up to $150, depending on the size and needs of your website. Popular managed WordPress hosting providers include WPEngine, Kinsta, Flywheel, and Pagely.
Besides hosting type, another thing that can influence the speed of your website for your users is the location of the hosting providers’ servers. Your objective should be to choose a server that is geographically closest to the places where most of your audience is present.
Choose A Theme Optimized For Speed
Using themes is so popular that it seems like the only way to build WordPress websites. While that may not be true, using themes does make things incredibly easier and it is highly recommended.
That is perhaps also the reason why building and selling premium themes has become a lucrative business opportunity. As a result of this, the web is currently flooded with thousands of free and premium themes. Unfortunately, not all themes are created equal.
This can make choosing the theme for your website confusing. Looking for a theme that is optimized for speed can, however, help you narrow down your list of possible choices by a large margin.
Two types of WordPress themes are optimized for speed:
- Themes that offer minimal and necessary features
- Themes that offer a variety of features, along with the ability to turn off unused features
As explained earlier, when a user tries to open a page on your website, everything associated with that page, including the WordPress theme features that it may or may not be using, need to load in order to display the page. That’s why, fewer active features are preferable.
It shouldn’t be difficult to guess which kind of theme is more pocket friendly. You can either spend your time looking for a lightweight theme that only offers the features that you require. However, keep in mind that you will need to be proactive as you may require additional features as your website grows.
In fact, that factor makes the second type of speed-optimized WordPress themes a better option than the lightweight theme. Spending a few dollars to avoid the pain of finding and migrating your website to a new theme after a few months or years is a wise decision if you can afford it.
Maintain A Clean Database
Over time, your WordPress data will accumulate a lot of information that will be obsolete or irrelevant. This will include the data of revisions, spam comments, fake user accounts, and other similar elements. As your database accumulates more and more junk, its size will increase and it will start putting the strain on your website’s performance. Moreover, a larger database will also increase the size and hamper the speed of your backups.
You can clean up your database manually using phpMyAdmin. However, the task requires a lot of technical expertise without which, you may end up causing more harm than good. If you have someone on your team with the kind of expertise and time required to perform regular database cleanups, delegate the task.
If, however, you don’t have this kind of expertise on your website, you can pay for a plugin that will automatically take care of this task for you. Some great examples of such plugins are Advanced Database Cleaner and WP-Sweep.
Maintain A Clean Media Library
Just like maintaining a clean database is important for optimizing WordPress websites for speed, maintaining a clean media library is similarly important.
Thankfully, deleting old and unused media files from your WordPress library is not as complex as cleaning up your WordPress database and can be done by almost anyone. With that said, if you don’t have the time, you can always use a plugin like Media Cleaner.
Make Sure Everything Is Updated
You may already know that WordPress is actually an open source platform. Thanks to the incredible demand it enjoys, the WordPress code is regularly updated by contributors.
These updates make WordPress more secure, introduce new and useful features, and most importantly, make the platform faster.
Just like the WordPress platform, the plugins and themes that are developed to be used on the platform may be updated frequently. Such updates may be especially frequent if you are using premium products as the developers have more incentive to make their products better.
The updates for plugins and themes are usually designed to make them compatible with the latest version of WordPress. However, a lot of times these updates are about fixing bugs, making the theme/plugin more secure, or simply reducing the influence they have on the speed of your website.
As the owner of your WordPress website, it is your responsibility to ensure both your WordPress version and the plugins and theme that you use are always updated to the latest version.
Get Rid Of Bad Plugins
Plugins are perhaps one of the best things about building a website on the WordPress platform. Just like themes, plugins also represent a great business or side gig opportunity for developers. As a result, for every imaginable task that a plugin can perform, there are several options to choose from.
However, not all plugins are made alike. While it isn’t totally clear whether the number of plugins associated with a website influences speed, the quality of plugins definitely influences the speed of your website. With that said, just to make sure you leave no stones unturned to improve your website’s performance, it is a good idea to be picky about the number of plugins you use.
If you have been operating WordPress for some time, there is a chance that you already have a few bad or unused plugins that you can get rid of. While you can easily identify the plugins you are not using, you will require help in identifying the bad plugins.
One of the best ways to determine how a plugin influences your website’s speed is to use a plugin (ironic, I know) called Plugin Performance Profiler or P3. P3 will scan all the plugins operating on your website and tell you exactly how much each of them is influencing your website’s performance.
Based on the suggestions from P3, you can choose to either uninstall the plugins or find lighter and speed optimized options.
Use A Content Delivery Network (CDN)
Before we talk about CDN, it is first important to know how the location of a server influences the load speed of your website. The closer a user is to a server’s physical location, the quicker load times they will experience.
This means, if your hosting service has hosted your website on a server in Singapore, your website will load much faster for users in South Asian countries, as compared to the experience of users in North America.
So how does a CDN fit in all this?
In simple terms, a CDN operates using a network of servers placed all across the globe. CSS, Javascript, and image files of your website are stored on this server. Based on the location of the users accessing your website, the CDN delivers the “heavy” content to them from the nearest server, effectively reducing load speed.
Using a CDN also reduces the load on your hosting server, since it is doing a lot of the work involved in serving website content to the user.
MaxCDN, now known as StackPath, is perhaps the most popular CDN used by WordPress users. Not only is their service equipped with the latest technology needed to improve content delivery times, it is also especially optimized to work well with WordPress websites.
StackPath CDN is also incredibly easy to use and install on your WordPress website, and is also compatible with popular caching plugins like W3 Total Cache.
Use Hosting Platforms For Videos
Using videos has almost become an absolute necessity if you want to attract and engage audiences. WordPress also offers the ability to upload videos directly to your website and play them using a HTML5 player. However, there are a number of downsides of doing this:
- It slows down your website as compared to other elements of your website, video files are much heavier.
- It puts undue load on your hosting service servers. So much so that hosting too many videos on your website may even lead to your getting blocked by your hosting provider, even if you pay for unlimited bandwidth.
- Having heavy video files on your website also increases your WordPress backup file size dramatically, making it difficult for you to restore WordPress from backup.
Thankfully, this challenge was identified quite some time ago and now there are several video and audio hosting services dedicated to overcoming it. Some popular examples are YouTube, Vimeo, and DailyMotion.
You can upload your videos to these platforms and embed them on your website. WordPress comes with a built-in video embedding feature so the process should be easy to execute. If you do find it challenging, you can find several tutorial videos on one of the video hosting platforms I just mentioned.
Use Excerpts
The default WordPress settings show each piece of content on your homepage in its entirety. This leads to two problems:
- It reduces the load speed for all the pages that contain a repository of other pages. This includes your homepage, category pages, and archive pages.
- It eliminates the need for users to click on the actual content and visit the page where it is hosted. As a result, the recorded page views for your content are less than the actual views it got. Moreover, this may also contribute to increasing bounce rates.
That’s why, it is recommended that you use excerpts of content instead of the full content.

This will help you speed up your website. Doing this is a pretty straightforward task. Go to the Settings section of your WordPress interface and find the “Reading” option.
Once you click on that, you will see an option called “For each article in a feed, show” with two options in front of it. Select “Summary” instead of “Full Text” and you are good to go.
Split Comments Into Different Pages
Getting a lot of comments on your content is usually a good sign as it indicates you have an engaged audience. However, getting many comments on your content also means that all the comments will be loaded every time a user opens a particular piece of content.
If your content is attracting several hundred comments, then there is a chance that it may affect the load speed of that web page.
Thankfully, the solution is quite straightforward yet again.
All you need to do is go to Settings>Discussion. Here you will see the option to “Break comment into pages”. Simply select the check box right next to this option and it is done!
Limit Post Revisions
Every time you revise a published post, the older version is saved in the database. This makes your database heavier and you guessed it, your website slower.
Here’s how it works:
Suppose you write a blog post that is 100 kb in size. Now, let’s suppose you update the content of this blog post on 4 different occasions. Now, the blog post and its revisions are taking up 500 kb of space.
While the numbers may look inconsequential in this example, they add up over time. To combat this problem, you can limit the number of revisions stored in your database.
To do this, simply open the wp-config file and add the following command to it:
define ( ‘WP_POST_REVISIONS’ , 4);
The number at the end of the code denotes the number of revisions that WordPress is allowed to store. In this case, the command allows it to store up to four revisions. To save more space and improve performance further, you can reduce this number and can even set it to ‘0’ or ‘false’.
We have now come to the end of the section dedicated to WordPress best practices to ensure optimum performance of your website. Following the tips shared so far will help you optimize your WordPress website to deliver the kind of performance it should deliver by default. In other words, these steps had nothing to do with how to speed up your WordPress website.
They simply ensured that the WordPress speed optimization tips shared in the next section will have the maximum impact when you implement them.
WordPress Website Speed Optimization Tips
This is where we talk about maximising the performance of your already speed-optimized website.
Without further delay, let’s jump right into it:
Optimize Images For Speed
In an increasingly visual digital landscape, images are like the lifeblood of your website. Having images on your website is important from the user experience perspective, it is important for ensuring conversions, it is important to ensure SEO performance, and the images you use can even influence the entire online perception of your business.
However, at the same time, image files are much larger than text files and when not optimized for use on your WordPress website, they can slow it down considerably. According to a study conducted in 2019, images make up (on an average) 34% of a website’s weight.
So, how do you optimize images for performance? The simple answer is, compression.
See, the images that most beginners upload to their WordPress media libraries and then, their websites, are usually very large in size. They need to be converted to web-friendly compressed formats like PNG and JPEG. In fact, those are the two of the most popular image formats used on websites all over the globe.
There’s mainly one difference between the two formats. PNG is less compressed as compared to JPEG. As a result of compression, JPEG images may lose some information and may appear to be lower quality than PNG images. On the other hand, PNG images, while sharper and more detailed than JPEG images, are heavier.
Confused about which format you should use for the images on your website? The correct way to deal with image optimization is to use a combination of PNG and JPEG images. Use JPEG images for most images and for those that don’t have rich colours and details. For the rest, use the PNG format.
To convert images to a desired format, without compromising too much on quality, you will have to depend on a quality plugin. Imagify, WP Smush, and ShortPixel are some of the best image optimization plugins currently available for WordPress websites.
Besides optimizing images, another way around is to not use images whenever possible. This may sound like controversial advice, but I am not asking you to stop using visuals on your website.
These days, a lot of websites have started using illustrations to improve aesthetic appeal and even communicate concepts and ideas. One of the reasons this practice has become popular is that in many cases, vector graphics are “lighter” than images.
Minify JavaScript, HTML, and CSS Files
As your website grows and new pages and functionalities are added, CSS, HTML, JavaScript, and other source code files grow heavier. As a result, there is more data to be transferred every time a user tries to load a page. More data transfer takes more time and slows your website down.
Minification does exactly what the term suggests, it minimises the code of your website. This happens by removing redundant elements like spaces, unnecessary characters, line breaks, and comments.
Minification makes sure that the backend of your website, just like its front-end, is optimized for user-delighting kind of speed. The best part is, minification can be done easily using plugins. The even better part is, there is an incredibly efficient free plugin that will take care of your code minification needs. It’s called Autoptimize and it works great!
Remove Render-Blocking For JavaScript and CSS
This is one of the more confusing findings that are often pointed out in website speed tests. This basically means that when a user opens a page on your website, the JavaScript and CSS code load before the rest of the website.
This is known as render-blocking. Basically, all the extra scripts are blocking your website from rendering until they are loaded, essentially making the experience for the user slower.
So, is render blocking necessary? To answer that question, let’s understand the function of JavaScript on your website. In most cases, it is used to perform an action on a webpage, like bringing up a popup. Loading a pop up before your page loads in anyway is a classic example of bad user experience. However, even if we ignore that, no popup is more important than the information on your webpage that the user is trying to access.
In other words, for most websites, render blocking is not necessary. The actions used to remove render blocking are known as defer JavaScript parsing and can be performed with the help of a plugin like WP Rocket.
Move Database Tables To InnoDB
This is one of the more technical tips in this article but still pretty easy to execute, in part.
The only things you need to understand here are:
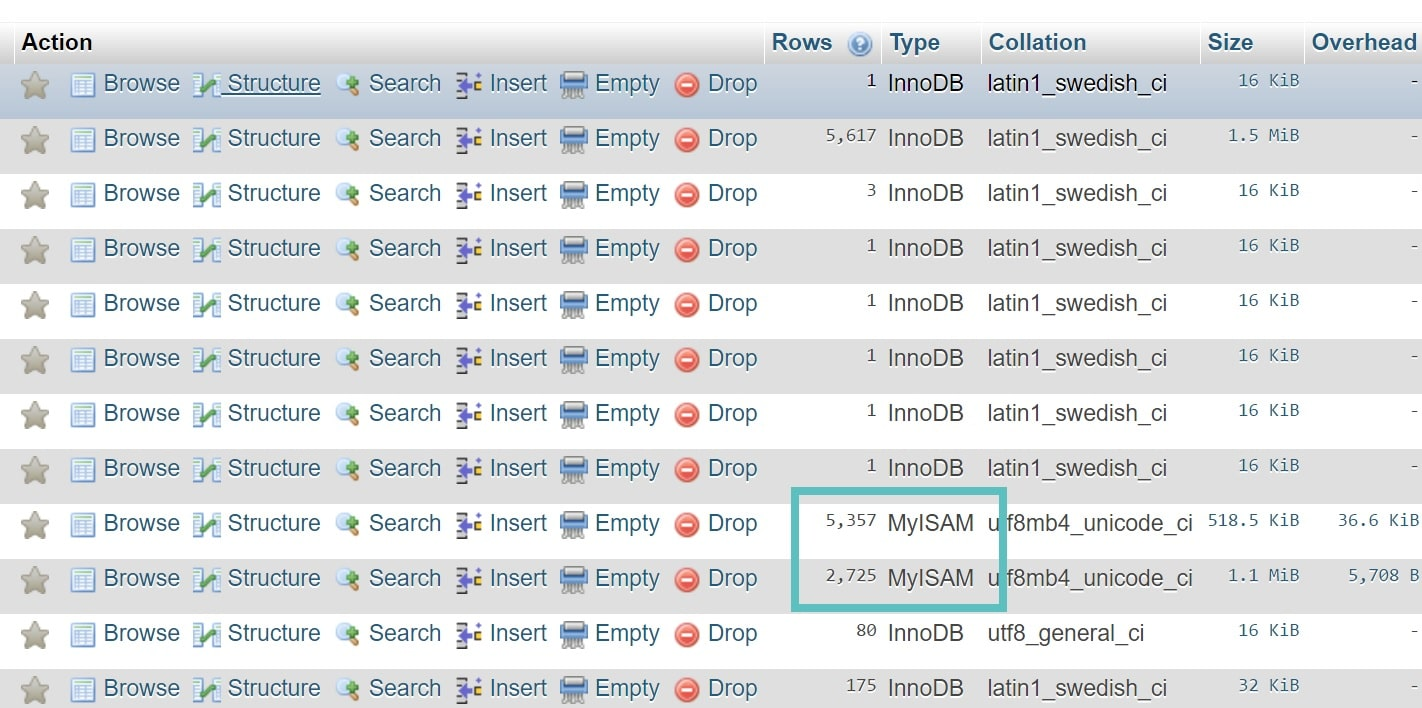
- Websites use storage engines. Older websites used MyISAM storage engines.
- Recently, it was discovered that another type, called InnoDB MySQL Storage Engine performs better than MyISAM storage engines and is also more reliable.
- Some older WordPress websites may still be using MyISAM storage engines, or a combination of MyISAM and InnoDB.
- If this is the case, transferring to InnoDB completely can improve the performance of your website.
Determining if your website is using MyISAM storage engines involves simple two step process:
Step 1: Log into phpMyAdmin and click on the ‘mydatabase’ option on the left side of the screen.
Step 2: On the resultant screen, scan the “Type” column which has information about the type of storage engine being used.
If you do find some instances of MyISAM being used, you can ask your hosting providers to conduct a migration to InnoDB. Most managed WordPress hosting providers will do this at no extra charge.
Install A Caching Plugin
When a user opens your website, displaying the website involves multiple steps. The process starts with a request going to WordPress from the user’s machine. Then, WordPress sends requests to your website’s PHP database and MySQL database. Once it receives the information, it then compiles everything in HTML and then, the webpage becomes visible to the user.
Even if you don’t know what most of the terms in the above paragraph mean, it is easy to see how this multi-step process can be time consuming. As a result, your website loads slower. The performance declines even further when there are multiple users trying to access your website.
Thankfully, the solution to this problem has been around long enough that it has been perfected and simplified. The solution is called caching and it can improve your website’s performance dramatically. Some claim that caching can improve the performance of some websites by up to 5 times!
Originally, caching instructions were added to the code of your website. These instructions would tell the users’ browser to download heavy files (JS, CSS, PHP files) to the user’s machine when they visit your website for the first time. As a result of this, the next time the user opens your website, they experience a much shorter loading time.
As mentioned earlier, this technology has been perfected and simplified. That means, there is no need to mess with the code of your website anymore, you can simply install a caching plugin and get the job done.
In fact, caching is so popular that many hosting providers including WP Engine and Bluehost offer it as a service. If that is the case with your hosting provider, you will not even need a plugin. However, if you do, the WP Super Cache is one of the most popular free caching plugins out there. It is incredibly easy to use and implement on a WordPress website and is equally effective.
Reduce The Number Of External Scripts
External scripts come in many forms including ads, tracking tools (like Google Analytics), or commenting systems (like Disqus).
Depending on the type of script and its function, certain scripts can put a heavy load on your website’s performance, essentially slowing it down.
For this reason, it is advisable to avoid using external scripts as much as possible. If you cannot get rid of all the external scripts on your website, make sure you are only keeping those that are absolutely necessary.
GZIP compressions is a compression technology (duh!) much like ZIP or RAR. It is used to compress the files of your website including HTML, CSS, and JS files.
Whenever a user opens your website, their browser requests your website’s data from your server. If the data has been GZIP compressed, it is much smaller in size and the data transfer is quick. As a result, your website loads quickly.
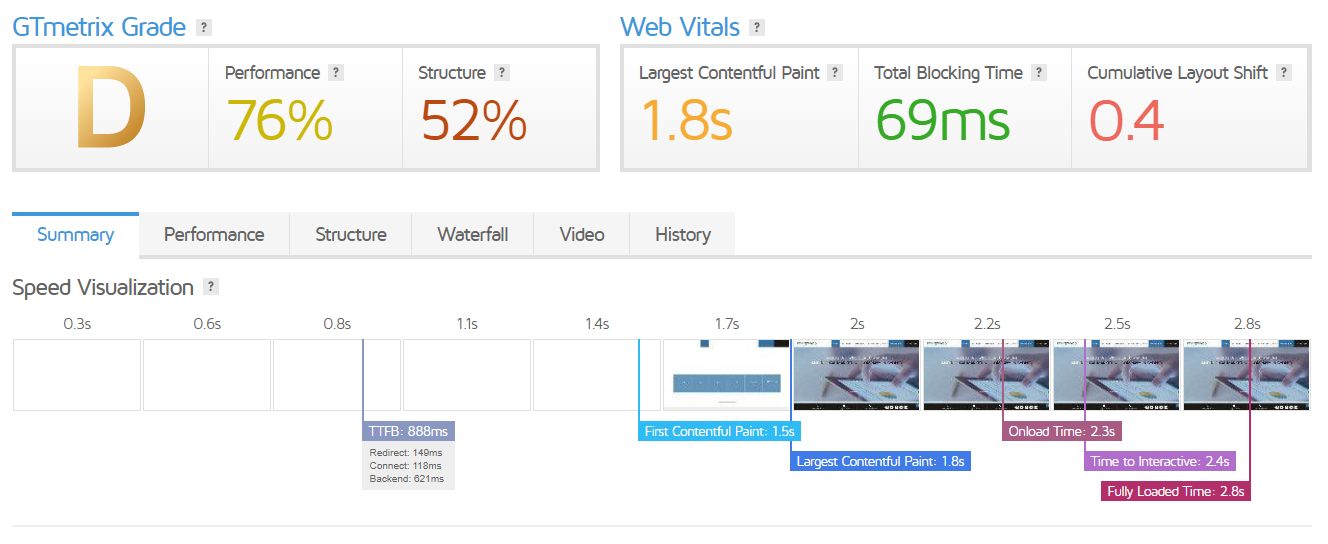
Checking whether or not GZIP compression on your website is easy. If you have already run a speed test on your website, as mentioned at the beginning of the article, you may already have this information.
If not, try running a website speed test in GTMetrix. If GZIP compression is enabled on your website, the results will look something like the following:
GZIP Compression
If, however, you don’t have GZIP enabled on your website, you can do it with the help of a plugin like W3 Total Cache.
If you have been following the advice shared in this guide, you may have already decided to download the plugin. However, if, for whatever reason, you want to avoid using a plugin for this job, you have two options:
- Find a hosting provider that offers GZIP compression by default.
- FInd a developer that can make changes to your website’s code and add GZIP compression to it.
Disable Pingbacks and Trackbacks
A pingback is a comment that is generated every time you get another webpage links to one of your webpages. Default WordPress settings also generate self-pingbacks in the cases where you link to one of your published pieces of content in a fresh piece of content being uploaded to your own website.
Over time, these comments get accumulated and add to the useless junk in your database, contributing to slowing your website down. Not to forget, after an initial few days, these notifications simply become annoying.
To disable pingbacks on your website, follow these steps:
Step 1: Log into your WordPress dashboard and go into ‘Settings’>’Discussion’.
Step 2: Locate and uncheck the option that says ‘Allow link notifications from other blogs (pingbacks and trackbacks) on new articles’.
Congratulations! You have just disabled pingback notifications from other websites. Now, to disable self-pingbacks manually, you will need to tinker with the source code of your website. You will have to access your WordPress theme’s “functions.php” file and add the following code snippet there:
function wpsites_disable_self_pingbacks( &$links ) {
foreach ( $links as $l => $link )
if ( 0 === strpos( $link, get_option( 'home' ) ) )
unset($links[$l]);
}
add_action( ‘pre_ping’, ‘wpsites_disable_self_pingbacks’ );
Remember that if not done correctly, this can cause your website to malfunction. If you want to avoid touching the code of your website, you can use No Self Pings Plugin (free) or Perfmatters (premium).
Lazy-Load Long Pages
These days, single page websites are becoming increasingly popular. If you have one, its performance can be optimized significantly with lazy loading. Even if you don’t have a single page website but have a long-form landing page or long-form content on your website, lazy loading can be beneficial.
Lazy loading delays the loading of all the elements present below the first fold of a webpage until the user actually scrolls down. This way, your server has to process fewer requests and load fewer elements of your website at a single time, enabling it to render your website at a much faster speed and improving the user’s experience.
If you are wondering how you can enable lazy loading on your website, the answer is one that has been repeated several times in this guide- by using a plugin. BJ Lazy Load is one of the most popular plugins that enables lazy loading for WordPress websites.
Pro Tip: You can also utilise lazy loading to speed up pages that may not necessarily be long, but contain a lot of images or external scripts.
Split Long Posts Into Different Pages
Users and search engine algorithms both love a long, detailed, and in-depth blog article. Even from a website owner’s perspective, a long-form article has a much better chance at ranking well in the Google
search engine result pages (SERPs) than a short article.
However, the ‘catch’ with long form articles is that they usually contain a lot of images that can potentially hurt the loading time for that web page. Even if you are optimizing your images as instructed earlier in this guide, too many images can still have a negative influence over the load times of your webpages.
One popular solution to overcome this website performance challenge is to split long articles into multiple pages. One of the reasons this method is so popular is that unlike many of the solutions mentioned in this guide, doing this does not require a plugin or an edit to the code of your website.
WordPress offers a built-in functionality to split long posts into multiple pages. All you need to do is open up a long-form post on the WordPress editor. Take your cursor to the point from where you would like to split the article and click the “+” button.
Next, select the option of adding a “page break” and voila! You are done.
If you are using the Classic Editor by WordPress, you can do the same thing by adding the “<!––nextpage––>” tag wherever you want a page break.
This method is easy and will be able to help most of you reading this guide.
If, however, you routinely published a lot of long-form blog posts, this method may turn out to be quite time consuming. Moreover, you may not always be able to split the content in equal chunks when you do it manually.
In such cases, you can utilise a plugin that automatically splits content into multiple pages when it meets certain criteria like a specific length.
The Automatically Paginate Posts plugin allows you to set the number of pages a post will be split in, and the number of words that will be displayed on a single page.
Use The Latest Version Of PHP
PHP is the programming language used by WordPress. The version your website is using can have great influence on its performance. Thankfully, upgrading to the latest version of PHP is quick, easy, free, and requires almost no technical knowledge.
That’s why, most good hosting providers take care of updating your website to the latest version of PHP automatically. To do it manually, implement the following steps:
- Log in to the PHP user portal and click on “Sites”
- Locate the environment name that you wish to change
- On the subsequent page, you will find a table with a column dedicated to the PHP version. Click on the number.
- You will find the option to upgrade or downgrade the PHP version in a pop-up window. Choose the option to upgrade.
Conclusion
Improving the performance of your website is not something that is necessary to gain an edge over the competition anymore. Having a quick loading website is a necessity in order to stay relevant in the fast moving world wide web. Thankfully, the WordPress platform is so amazing and popular that there is a lot website owners can do to ensure they are delivering a delightful experience to their users.
When it comes to optimizing WordPress websites for speed, it is first important to ensure they are running on their full potential with default settings. Once you have made sure your website is developed and functioning with all the best practices in mind, you can move on to the optimization.
Both aspects of improving website load speed were discussed in this article. This was all advice derived from my own experience of working with hundreds of WordPress websites.
However, if you think I have missed mentioning an important website performance optimization technique, tell me (and everyone else) about it in the comment section below.
FAQs
What Is A Good Website Speed Score?
According to Google, a score above 90 is considered good. The Google Pagespeed Insight is a popular tool for checking the page speed of your website. It gives your website a score between 0 and 100; a score above 90 means it is optimized for speed and user experience.
To check the speed of your website, you need to go to the Pagespeed Insight tool, enter your website URL, and click on analyze. Once analyzed, you will get a speed score for the mobile version and desktop version of your website.
How Do I Increase Page Speed In WordPress?
- Hosting plan: Select a reputable hosting provider for fast servers and good performance.
- Select the theme carefully: Choose a well-coded and minimal theme for WordPress. Complex themes can make your website slow.
- Minimize plugins: Minimize the number of plugins you use and only keep the essential ones.
- Optimize database: WordPress will collect a lot of databases over time. Regularly clean up your database using plugins such as “WP-optimize” or “WP-Sweep.”
- Use content delivery network: Use CDN services like Cloudflare to distribute your website’s assets (images, CSS, javascript) to reduce user load time.
Why Is Page Speed Important For SEO?
Page speed is an essential factor that impacts how a search engine ranks your page. Even though it is not the only metric in SEO, it is an important part.
Websites with a higher page speed score will likely rank on top of the SERPs. While content quality and relevance are essential, page speed can’t be overlooked. Search engines index Fast-loading pages more efficiently, which helps improve SEO.
Moreover, the fast page speed improves the user experience, making your audience more likely to stay and engage with your content.