5. Find Backlink Opportunities In Resource Pages
Pages that list the best resources around a topic are known as resource pages. Since most resource pages point to content on other websites, they are great from a backlink building point of view.
One of the biggest challenges with securing backlinks on resource pages is finding the right resource pages. It is possible to overcome this challenge by using Google Search Operators in conjunction with a little bit of creativity.
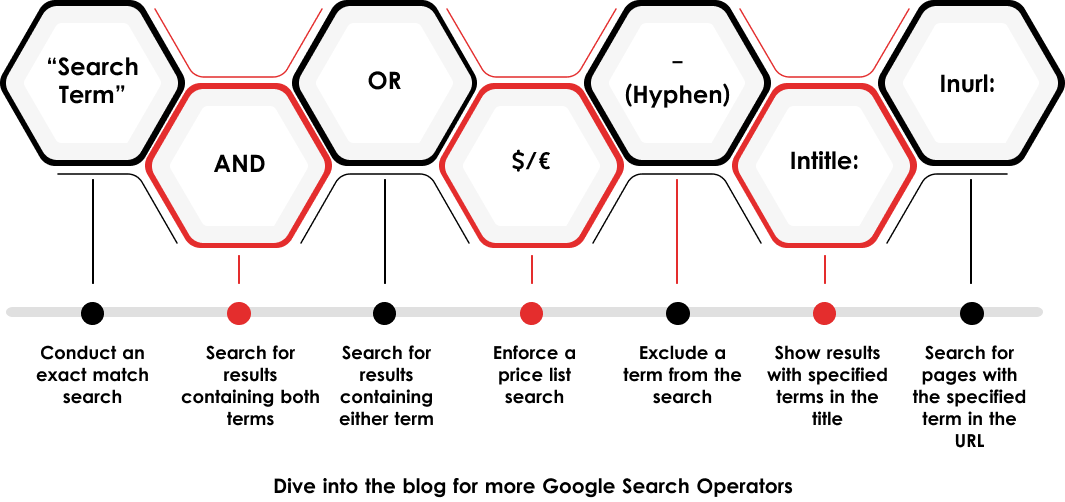
The simplest solution is the following command:
<industry> [intitle:Resource | inurl:resource]
While this may return some useful results, it will also return a lot of useless, irrelevant results.
You can narrow down the results further with a command like this:
<industry> [intitle:resource AND inurl:resource]
If you create infographics as content or marketing assets, and want to look for backlink opportunities using those, you can use a similar command:
<industry> [intitle:infographic AND inurl:infographic]
Similarly, you can also look for specific infographics by replacing in the above command, with specific text. Something like this:
“How to do a deadlift” [intitle:infographic AND inurl:infographic]
Uncover backlink opportunities and enhance your website’s authority.