Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Multiregional and Multilingual SEO: Definitions
- Choosing The Right Locations To Target With SEO
- The Importance Of Choosing The Right Domain And
URL Structure - Webmaster Tools Geotargeting
- Taking Advantage Of A Shared Database
- Multilingual Marketing
- Bonus Section: Common Multiregional SEO
Mistakes That You Should Avoid - Conclusion
Introduction
Among the many revolutionary things that the web has made possible, improving the potential reach of business is definitely among the best. Small businesses that were often limited to serving customers in their local areas have started attracting orders and requests for their services from different countries. The power of the web to reach people, combined with the improved affordability of international logistics have opened up a whole new world of opportunities for businesses all over the world.
With that said, taking advantage of this opportunity is a daunting challenge, especially from a search engine optimization perspective. This is because optimizing a website to perform well in search engine results shown in different regions of the world, using different languages, is quite different from doing regular SEO.
In fact, it is often so different that marketing for multilingual websites or websites that want to target different but specific locations has emerged as a separate specialization.
If you are thinking about moving into this niche and providing multilingual SEO services, this guide will tell you everything you need to know about the subject.
Let us begin by understanding the definition of multiregional and multilingual SEO:
Multiregional and Multilingual SEO: Definitions
Multiregional SEO is the practice of optimizing website content with the objective of making it rank higher in the SERPs displayed in specific target locations. Similarly, multilingual SEO is the practice of serving optimized website content in different languages.
In most cases, the need to do multilingual and multiregional SEO overlap. Meaning, companies that are targeting specific cities and countries often require their content to be optimized in the local languages of those areas.
In such cases, besides taking care of the regular SEO ranking factors, marketers and SEOs must also ensure that they are optimizing the website in a way that search engines understand that it is trying to target specific locations and languages with specific web pages.
Take a look at this table depicting the distribution of internet users all over the world:
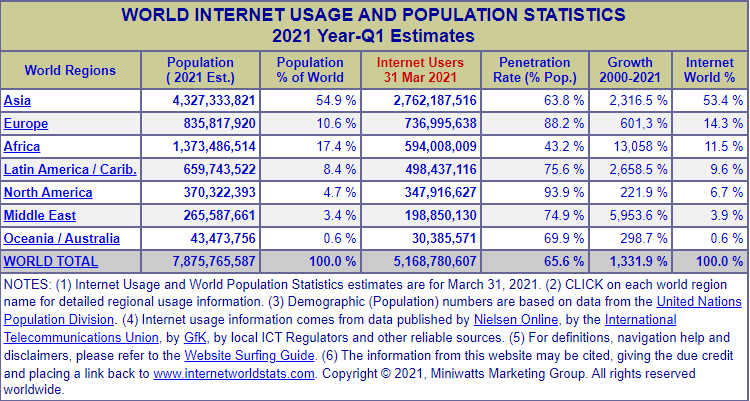
As you can see, even the continents that contribute low percentages have hundreds of millions of users. So, if your business is succeeding in your company, venturing into foreign markets makes all the sense in the world.
Before we can discuss the factors that search engines like Google take into account to understand targeted locations for a website, it is important to understand how to pick the right locations to target with your website.
Choosing The Right Locations To Target With SEO
Before you can begin optimizing your website to rank at the top of the SERPs in foreign countries, you must first ensure that you are indeed targeting the correct regions.
For instance, if you are selling winter coats in the UK, venturing into Spain may not make a lot of sense, since Spain mostly gets warmer weather. On the other hand, venturing into the German and Eastern Europe has great potential to deliver delightful returns.
While some common sense can help guide the decision of choosing the right locations, there is another great way to choose them.
Let’s understand this with our example of winter coats in the UK. So, common sense and understanding of the product tells us that countries that get cold weather are the right targets. However, if you have to prioritise, how will you decide whether you should target Germany or Switzerland?
The answer lies in some good old keyword research.
Any good SEO tool or keyword research tool will let you look at the keyword performance metrics for specific locations. In the case of our example, a comparison between the search volumes for ‘winter coats’ in Switzerland and in Germany will tell you where there is a higher demand and a lower competition on the search engines.
If you are struggling with the step that comes before you can start comparing keyword search volumes and competition in different locations, you can simply search for a keyword (using the keyword research/SEO tool) and look at the search volumes of that keyword in different countries.
Then, you can compare the average competition for those keywords in the locations or countries with the highest search volumes and select the right locations for the expansion of your business.
In some cases, you may notice that your keyword research or SEO tool consistently shows low search volumes in specific countries like Russia or South Korea. This may be the case because in these countries, Google is not the most popular search engine.
If you don’t have an SEO tool or a keyword research tool, another great place to verify whether a foreign location is right for your business is Google Trends. Google Trends, as the name suggests, will tell you about the search trends related to any term you enter into the tool.
The best part is, Google Trends lets you filter results by location. Here’s the Google Trends graph for the term ‘winter coats’ with location set to Germany:

Here’s how the same graph varies when the location is changed to Switzerland:
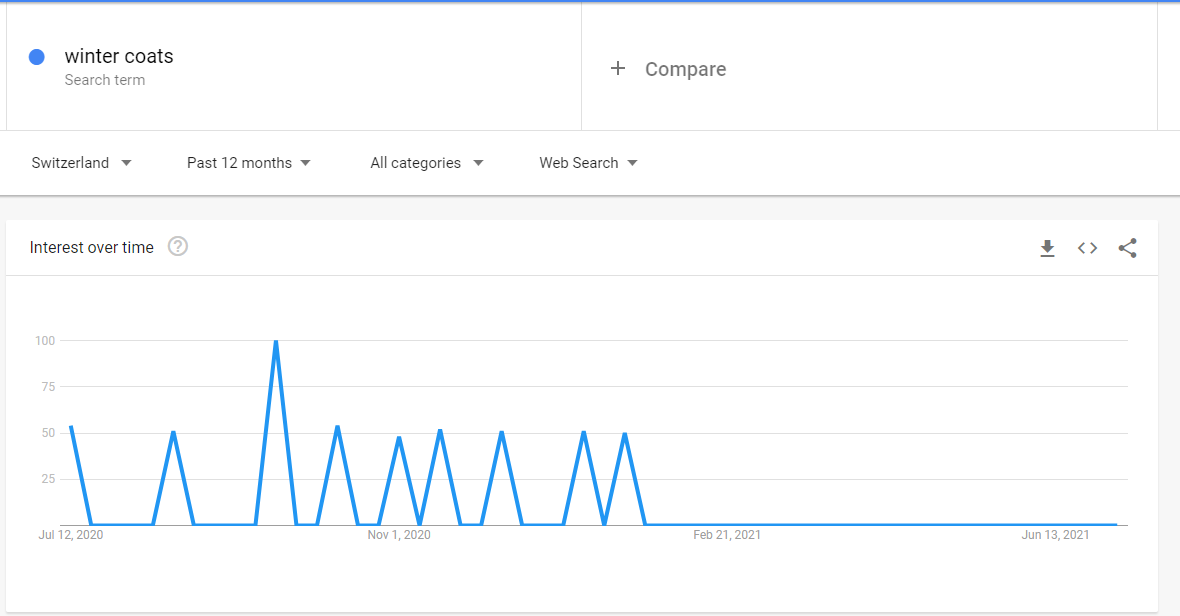
Such a comparison of different locations should enable you to make an informed decision about expanding into new locations.
Deciding the target locations (and languages) is the most important and the first step of doing effective multilingual and multiregional SEO. Let’s look at the next one.
The Importance Of Choosing The Right Domain And URL Structure
As mentioned earlier, Google and other search engines use a variety of website elements to gauge which locations you are trying to target with a specific web page. However, since search engines utilise ‘web crawlers’ or algorithms programmed to understand different websites, they are not always 100% accurate in determining the location you are trying to target with your content.
Google has even gone ahead and directly told everyone that “it is difficult to determine geotargeting on a page by page basis” and that they want website owners to “consider using a URL structure that makes it easy to segment parts of the website for geotargeting”.
To put it into simpler words, Google (and other search engines) face a difficult time in determining the geotargeting of your website with the elements present on your website. As a solution, they recommend using URL structures that make it easier for them to decipher this information.
So how can you use the URL structure to help search engines understand the geotargeting of your website? There are actually a few options that you can choose from:
Country Code Top Level Domains (ccTLD)
These are domains that have country codes in place of the generic extensions like .com. So, if, say, you are looking to expand into France, your ccTLD will be website.fr instead of website.com.
According to Google, using a ccTLD is interpreted as a strong signal that a website is targeting a specific country. However, if you already have a website with a generic domain extension, adding multiple ccTLDs may make doing SEO and tracking SEO performance a challenge.
With that said, if you are definite about targeting a single location, using these extensions is strongly recommended. Even Google uses ccTLDs to segment their own website according to the location. Here are a few examples that are currently being used by Google:
- Google.co.uk
- Google.co.in
- Google.fr
Subdomains Combined With Generic Top Level Domains (gLTDs)
Generic top level domains are the ones that we are used to seeing, they end with a generic extensions like:
- .com
- .org
- .biz
- .edu
- .gov
- .mobi
- .jobs
As the name suggests, generic top level domains don’t target specific locations. However, they can be used to target specific locations using location-specific subdomains. Here’s an example:
Fr.website.com
Once again, such URLs are also used by top websites like Facebook. Here’s what Facebook’s URLs look like in different locations:
- Fr-fr.facebook.com
- En-gb.facebook.com
Using a subdomain to segment your website content in different languages is a superb way to both tell the search engines about the locations you are targeting, while also not turning your SEO tracking tasks into an analysis nightmare.
gLTDs with subdirectories
Using subdirectories is another popular way to segregate website content meant for users in different locations. A URL using gLTDs with location specific subdirectories looks something like this:
website.com/fr/
website.com/en/
This style of URL is also used by a number of popular websites, including the tech giant Apple. Here’s what Apple’s URLs look like in different countries:
www.apple.com/fr/
www.apple.com/de/
The main two benefits of using subdirectories over subdomains are:
- It is easier to manage and update website content
- The authority gained by each subdirectory is also transferred to the main domain name
With that said, if you are planning to use gLTDs with subdomains and subdirectories, you will also have to use webmaster tools to specify your website’s geotargeting.
Webmaster Tools Geotargeting
Thankfully, using webmaster tools to set geotargeting is a fairly straightforward process. Simply follow these steps:
Step 1: On the webmaster tools homepage, select the desired website
Step 2: Click on “Site Configuration” option and find and click on “Settings”
Step 3: Find the “Geographic target” on the resulting page and select the desired options
Choosing the right URL structure strategy to specify the geotargeting of your website will depend on your (or your team’s) technical capabilities and your ability to handle complex data.
For your reference, here’s Google’s comparison of the pros and cons of all the options mentioned above:

With URL structures optimized for multiregional and multilingual SEO, let’s look at the other ranking factors.
The Big Question: Does Server Location Matter?
For a long time, it was believed that choosing a server close to the location of your target audience is enough of a signal for search engines to understand which locations you are targeting with your website. This belief was not misplaced. Google has confirmed that up until a certain point in time, they used the location of the servers to determine the geotargeting of a website.
However, things have changed now. For one, just like small businesses, hosting service providers have also expanded their businesses to countries that are thousands of miles away from the country of their origin. Another big change is the fact that modern hosting giants now have servers spread across multiple different locations and website owners don’t always have the option or the know-how to manually specify their desired server location.
The biggest change with respect to using server locations to determine geotargeting has occurred due to the rise of content delivery networks or CDNs.
CDNs save website data and content on multiple servers and deliver them to the user from the server that is physically closest to them. As a result, website content is distributed all over the globe and is sourced from different servers to serve users present in different locations.
This means that using server locations may still be a factor used by search engines to determine the geotargeting of a website. However, it is certainly not an important factor and should not influence your choice of hosting providers.
Using the hreflang Annotation/Markup
When used correctly, hreflang tags can help search engines present the most apt content to the user, based on their location and preferred language settings.
The obvious use of hreflang tags is to let users consume your website content (like blog posts) in their preferred language.
The less obvious but equally awesome application of the hreflang annotation can be seen in the case of ecommerce websites that operate in multiple countries. Using these tags, the website is able to present the cost of the listed products in the currency that is popularly used in that country.
Another big advantage of using the hreflang tag on your website is that it will help you solve duplicate content issues that may occur when you have different language versions of the same website.
Here’s a list of things that you must keep in mind in order to correctly implement a hreflang markup on your website:
- You have three options for where you can place the hreflang tag. Your sitemap, or the
of your HTML page, or the HTTP headers. Make sure you are placing the tag in only one of these places. - Make sure all language variations have the exact same hreflang annotations placed on them.
For the locations or languages that you have not specified, make sure you are using hreflang=”x-default” annotation. - For languages, make sure you are using the ISO 639-1 code. For locations, use ISO 3166-1 Alpha 2.
Another thing that you must remember while using hreflang tags is that they are not a definitive solution. At the same time, they are an important signal for search engines in the case of websites that are targeting multiple locations and languages with their content. Google has published a detailed guide on the correct use of hreflang tags, make sure you check it out here.
Taking Advantage Of A Shared Database
Using a content management system is not a necessity to do effective multiregional and multilingual SEO. However, using one does make your job much easier. Most leading content management systems (CMS), including WordPress, Drupal, and Magento offer support for multilingual websites. All these CMS come in-built features that support a multilingual SEO structure on a shared database.
One of the most pressing advantages of using a CMS on a multilingual website is that it lets you configure your website with multiple domains, or sub-domains, or sub folders (depending on the choice you made in the first step) using the same database. This means, when you update an element on one version of your website, it will automatically get updated on all the different versions of your website.
Implementing such updates manually can take hours worth of mundane work but having a CMS on your side will definitely make things easier.
Another advantage of using a CMS that automatically updates changes on all the different versions of your website is that it will eliminate the room for human error. Managing multiple websites can get overwhelming for even the most efficient managers. This may sometimes lead to mistakes like listing of old or discontinued products on one version of your website.
Finally, a big SEO advantage of using a CMS is that it allows you to link your website pages with equivalent pages in a different language, effectively helping you strengthen the internal linking profile of your website.
Translating Your Website
Finally, it is time to translate your website. However, it isn’t as quick or easy as you may have imagined.
In the past few years, language translation technology has made some serious strides and as a result, tools like Google Translate have seen stark improvements. However, there is still some time (a few years, maybe) left before these tools can effectively translate content that is fit for marketing.
Google says (and I agree) that automatic translations are rarely accurate and often don’t make sense. As a result, it makes the user experience worse, and Google absolutely despises bad user experience. That is perhaps why they have warned that automatically translated pages may be viewed as spam.
This means, you will have to find a translation expert to do it manually. It may take more time and demand more investment than a translation tool but it is a non-negotiable requirement.
Even when you have found someone to translate your website, the matter of using the correct way for including keywords in your content remains.
Here’s how you can find the right keywords in different languages and optimize your website to rank for them (for the sake of this example, we will talk about translating from English to French):
Step 1: Identify the keywords you want to target in English. Make sure you have identified a primary keyword, and a couple of secondary keywords.
Step 2: Translate your English keywords to French. Then, use a keyword research tool to find similar keyword suggestions of Spanish keywords.
Step 3: Map the keyword suggestions and identify which keywords align with which pages on your existing (English language) website.
Step 4: Translate the content of your website. Don’t think about keywords or SEO at this point.
Step 5: Besides making sure that the translation is absolutely on point, make sure that you are using the units of measurements, names of places, currencies, and phrases that your French audience understands and find relevant.
Step 6: Once the translation is complete, optimize the French web pages with corresponding keywords you found in the previous steps. Make sure you are using your primary keyword in the headers, the meta title, and the meta description at least once. Wherever possible, try to also include your secondary keywords in the meta titles and descriptions. Also make sure you are (sparingly) using your primary, secondary, and supporting keywords in the content naturally. If they don’t make sense, it is okay to skip including them in the content.
Step 7: Translate your URLs but make sure that you are not including any alphabets with accents. If you are using a CMS that supports multilingual websites, you will easily find addons that will allow you to translate your URLs and make them SEO friendly by removing accents.
Pro Tip: I strongly recommend finding a translation expert that resides or has lived in the country that you are planning to target. Doing this will allow you to publish content that isn’t just accurate in terms of language, but also appeals to the local culture of your target country. This will happen when your content uses phrases and lingo that only locals use and understand. Similarly, make sure that your content is making references that are both, relevant to your brand and understood (and appreciated) by your new audience.
Why is this important?
It is a well known fact that having content that delights your users has a direct (positive) impact on your website conversions. However, many don’t realise that delightful website experience also contributes to better SERP performance for your website. This is because Google has all the tools it needs to gauge the general perception of the experience on your website. They dominate not only the search engine market, in many cases, Google is also responsible for telling website owners about the user behaviour on their website using Google Analytics. This means that they have plenty of data about how users interact with the content on your website. If that’s not enough, Google also controls nearly 60% of the browser market with Google Chrome. It is a safe assumption that Google has the ability to use Chrome data to further understand user behaviour.
If your website is delighting users, Google will know and it will reward you with higher search engine rankings and more organic traffic. If it’s not, Google will still know and will ensure that it is directing its traffic to a delightful website.
Multilingual Marketing
If you have followed all the steps laid out in this guide so far, you have successfully developed and published your website. However, that is just the first step of running a multilingual marketing campaign, at least from an SEO point of view.
To really rank your website at the top of the SERPs in your targeted locations, you must “market” it. Marketing it on search engines usually boils down to:
Providing a positive user experience. We discussed the importance of a positive user experience in the previous section (check out the Pro Tip). It not only improves your chances of converting a website visitor into a paying customer, it also improves your website’s average dwell times and reduces bounce rate. As a result, your website appears higher in the search results and gets more organic traffic. If you have followed all the steps laid out in this guide, you may already have a delightful website in all your targeted languages.
Optimizing the on page elements of your website for search engines. Once again, if you have followed all the steps discussed before this section, your website is already optimized in a way that search engines will be able to decipher the locations and niche that you are targeting. However, I still recommend conducting a website SEO audit to ensure you have optimized for every on-page ranking factor.
Link building for SEO. This is the part that you still have to perform. If, at the beginning of this guide, you chose to create subdirectories instead of subdomains or gLTDs, your translated website may be able to benefit a little from your existing links. However, these benefits will deliver negligible results at best.As you may already know, Google has published clear guidelines for collecting backlinks. These guidelines dictate that the backlinks pointing to your website must be natural, and must come from relevant, high authority websites. THis means, if your website that caters to English speaking countries is attracting links from, say, a Chinese website, Google will view it as link spam and may end up serving you with a penalty or even disavowing your entire backlink profile.Similarly, if you have created a website in French, your existing links that come from English language websites will not benefit it. You will be required to do manual link building for your French website from other websites that predominantly use the French language.
Bonus Section: Common Multiregional SEO Mistakes That You Should Avoid
As you may have realised, multilingual and multiregional SEO is a complex undertaking and it is common for beginners to make mistakes. However, since you are reading this article, you have the chance to learn from the mistakes that I made as a beginner and avoid making the same blunders.
Let’s look at what these mistakes are:
Not Giving Users A Choice
Many websites automatically redirect users to their version of their local website even when they try to look up the main website. While it may make sense in a handful of cases, it actually has a number of downsides. The most pressing one is that redirecting users will mean that you are also redirecting Google.
Google doesn’t have specific bots for specific countries and if your website automatically redirects someone to the English version just because of their location, it will mean that the Googlebot will face the same experience and will not be able to properly index the other versions of your site.
Automatic redirections may also result in confusions among users that are not tech savvy and it may also lead to bad experiences for users that are simply visiting a foreign country.
Using Automatic Translation
As mentioned earlier, automatic translation tools are not (yet) capable of producing coherent translations that make sense in different languages. As a result, Google has warned that websites that use automatic translations will be marked as spammy websites.
If you are expanding to a new market, it pays to do everything right, and it is especially important to get your content right. From helping you achieve better rankings in the local search results to helping your website delight and convert visitors into customers, your content is perhaps the most important cog in your marketing machine.
Not Translating The Non-Visible Elements Of Your Website
During translation, many website owners overlook the website elements that are not directly visible to the users. Some do it because they think if nobody can see the content, it doesn’t matter. Others simply end up overlooking these elements because they are not readily visible on their website.
However, these bits of content present in your image alt texts, meta descriptions, meta titles, URLs, pop-ups, sign up forms, and checkout pages may not be visible but they contribute a lot to the visitor’s experience on your site.
Some elements like the image alt text, meta titles, and meta descriptions are also used by search engines to better understand your website and the content present on it. That’s why it is important to ensure you are also translating all these elements along with the rest of the content on your website.
Not Producing Locally Relevant Content For Different Websites
After your website has been translated and launched in a different country or region, it is important to understand that you cannot always publish translated versions of your content to your new websites. In some cases, it may work.
However, if you truly want to entice a new audience, you will have to generate content that appeals to them, their unique cultures, and the events and trends that are popular in that country. If you keep feeding them content that you are sharing with your English speaking audience, building a local ‘tribe’ in a new region will be incredibly challenging.
Conclusion
There you go. Everything you need to know to get started with and crush the competition with your multilingual and multiregional SEO strategy. As mentioned earlier, implementing such a strategy is challenging, even for seasoned SEO professionals.
If you agree, we can help your business with expansion in new markets. We have done it for our own agency and we currently have a presence on four continents. We have helped hundreds of clients achieve similar results. We’re confident that we can also help you. But you don’t have to take our word for it. Get in touch with us and let us prove it to you.
FAQs
Why Is Multilingual SEO Important?
Having content that delights your users usually positively impacts your website’s conversion rate. Moreover, a delightful website experience also helps your website’s performance on the SERPs. With multilingual SEO practices, you can prepare your content in a language the local audience uses, boosting user experience.
Search engines like Google can know when your website offers visitors a delightful experience. So, it rewards you with better search engine rankings and helps you get more organic traffic. Multilingual SEO practices help you achieve these results.
What Is The Advantage Of A Multilingual Feature In A Website?
Having a multilingual feature on your website can benefit you in the following ways:
- It boosts search engine visibility by addressing the search queries written in local languages
- It helps build trust and credibility for your website among the non-English-speaking population
- It improves international traffic and engagement on your website
- It boosts overall user experience as visitors can now consume your website content in their preferred language
- Better user experience due to multilingual SEO leads to a better conversion rate
- It ensures clear and precise communication
What Is the Difference - Multilingual vs. Multiregional SEO?
Multilingual SEO practices focus on optimizing website content for different languages, while multiregional SEO practices help you optimize your website content for specific regions.
Since the users in different regions use different languages, the multilingual and multiregional SEO strategies often overlap. While the practices may be slightly different from each other, the objective of both these SEO strategies is to help your website rank higher.
How To Do SEO For Multiple Languages?
To conduct search engine optimization of your website for multiple languages, follow the steps below:
- Identify your target market and learn what languages are used in those regions
- Conduct keyword research for those selected regions
- Decide the URL structure for your websites. Having separate domains, subdomains, or subfolders for separate countries will be helpful.
- Translate and optimize your content for the target keywords
- Optimize the title tags as per the chosen languages
- Fix the meta description as per the selected language
- Build backlinks from high-authority websites